Stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) is a minimally invasive procedure used to find where seizures are coming from in the brain. Using a robotic arm, neurosurgeons can place multiple electrodes deep in the brain through a very small incision. The information from an SEEG can help determine the best treatment plan for a child with epilepsy and develop a precise surgery plan if resection surgery is an option.
At Le Bonheur’s Neuroscience Institute, neurosurgeons use the ROSA One Brain technology to conduct SEEG. This robot provides neurosurgeons with very detailed planning before the surgery and precise, safe placement of the electrodes resulting in a highly effective way of targeting areas that may be responsible for seizures.
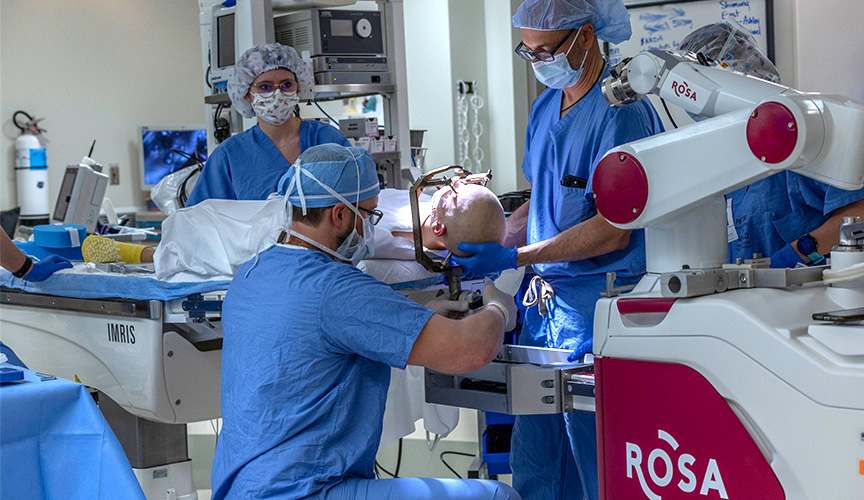
How SEEG with ROSA One Brain Works
With ROSA One Brain, neurosurgeons have pinpoint guidance before and during surgery. Prior to surgery, ROSA combines a child’s MRI, CT scans and any other brain imaging to create a comprehensive 3D map of the patient’s brain and head. Using these maps and ROSA’s software, neurosurgeons create detailed SEEG plans for where to place electrodes so that they reach precise areas of the brain while avoiding areas that control important functions like speech and movement.
In the operating room, ROSA scans the patient’s face to match it to the 3D map of the brain and head that was created before surgery. ROSA then guides the surgical instruments to precise locations based on the surgical plan created by the neurosurgeon with ROSA.
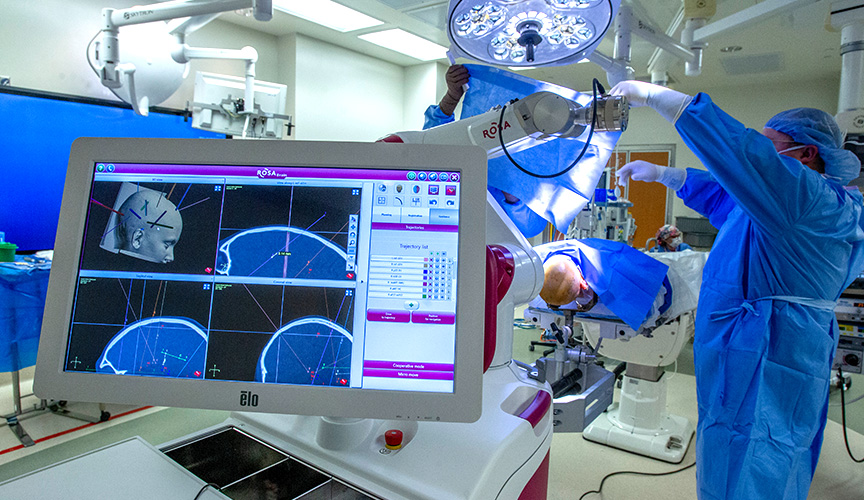
With an incision of only a few millimeters, the neurosurgeon can place an electrode into the brain. The number of electrodes depends on the patient but can range from six to 12 in one SEEG procedure. An EEG machine in the operating room confirms that the electrode is in place and working. After surgery, the patient’s head is wrapped with a bandage, and they are sent to Le Bonheur’s Epilepsy Monitoring Unit (EMU).
Removing the electrodes is a simple process – either in the operating room followed by surgery to remove the seizure focus or under light sedation with one stitch to close the incision if no further surgery is needed.
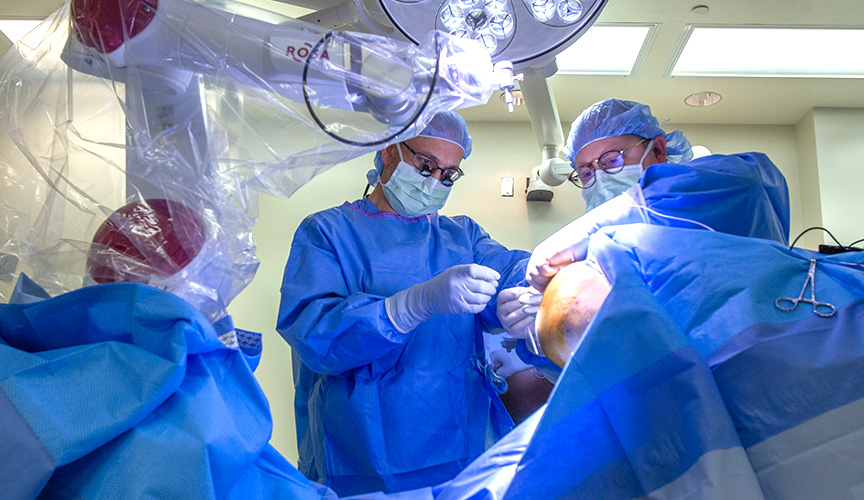
Benefits of SEEG with ROSA One Brain
Using SEEG with ROSA One Brain to identify seizure areas of the brain provides many benefits for patients and neurosurgeons.
- The minimally invasive nature of the procedure means a faster recovery for patients and a lower risk of complications.
- Quick placement of each electrode means less time under anesthesia. Previous electrode placement methods could take hours. It can now by done typically within 90 minutes.
- The robot arm (ROSA One Brain) provides highly accurate and safe placement of electrodes.
- Neurosurgeons can target multiple areas within the brain covering more space. This also allows them to reach areas previously difficult to access in hopes of uncovering the networks that lead to the child’s seizures.
All of these benefits combine to give Le Bonheur neurosurgeons and neurologists the best chance to find the areas where seizures are coming from and create the best treatment plan for each patient.




